What happened, and who agreed
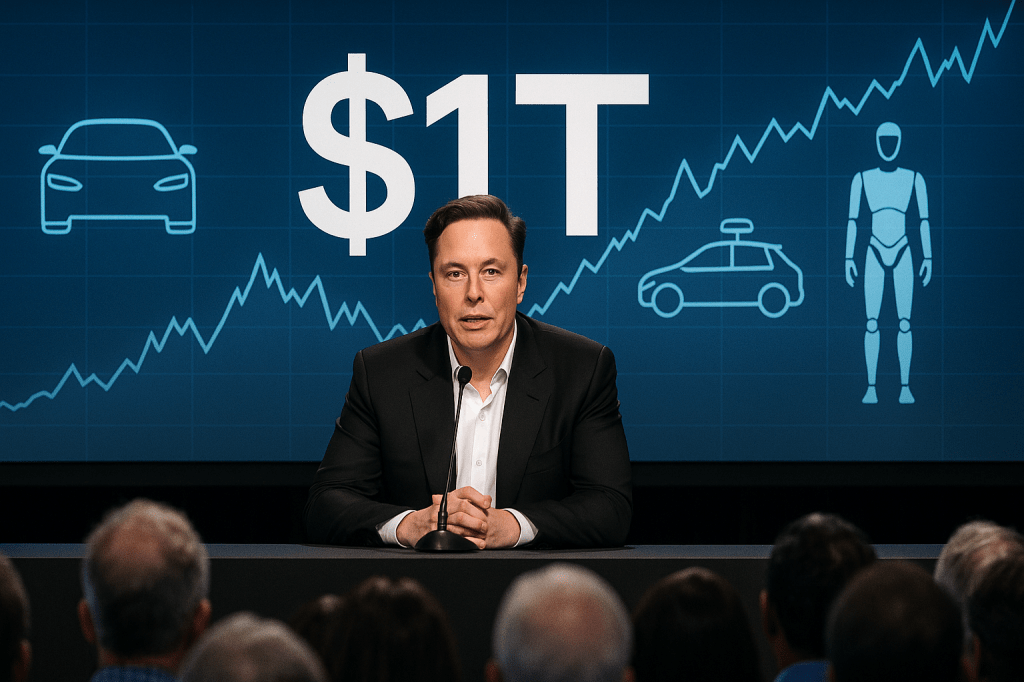
Tesla shareholders voted to approve a new pay package for CEO Elon Musk, with more than 75 percent of shares cast in favor according to the company statement on the vote outcome. The package could award Musk up to 423 million additional Tesla shares if Tesla meets a set of ambitious performance targets over the next decade.
The deal has been described as the largest potential corporate payout in history, with headline estimates reaching roughly one trillion dollars if all milestones are met and shares reach their target values. The vote took place amid ongoing legal disputes about earlier pay awards and active debate among investors and governance advisors.
Key facts up front
- Shareholder vote result, initial count: over 75 percent in favor; final tally will be filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
- Package size: up to 423 million new shares, which could bring Musk close to a 25 percent ownership stake in Tesla if those stock grants are fully issued.
- Major performance requirements include a ten year stretch to raise Tesla market value from about $1.5 trillion to $8.5 trillion, deployment of one million robotaxis, sale of 12 million additional cars, one million humanoid robots, and 10 million Full Self Driving subscriptions.
- Legal context: a Delaware court previously invalidated an earlier Musk pay package because of concerns about the board’s independence, and Tesla is appealing that ruling to Delaware’s highest court.
- Corporate governance item: shareholders also approved a measure to change Tesla’s legal home to Texas.
Why this matters to ordinary people
This vote touches on several areas that affect the public. First, executive compensation at large companies shapes how top leaders are rewarded for long term strategy versus short term stock moves. Second, the package ties Musk’s pay to outcomes in electric vehicles, autonomous vehicle services, and humanoid robotics; those areas could influence jobs, transportation options, and consumer technology in coming years. Finally, the vote and surrounding legal fights raise questions about corporate governance, investor protections, and how boards oversee founders and founders who hold large voting power.
Simple definition: market cap
Market capitalization, or market cap, is the total value of a company’s outstanding shares. The package asks Tesla to grow that number from about $1.5 trillion today to $8.5 trillion within ten years to unlock part of the award. That is a large increase in size and value.
What the performance milestones require
The plan has many distinct targets that Tesla must hit before Musk receives large tranches of stock. These are not based only on profits. They mix sales, subscriptions, technological deployments, and market value.
- Market cap target: increase Tesla’s market value from the current range near $1.5 trillion to $8.5 trillion within ten years.
- Vehicle sales target: sell 12 million additional cars over the period of the award.
- Autonomous vehicle target: deploy one million robotaxis. A robotaxi service would use autonomous driving technology to carry riders without a human driver.
- Software subscriptions: reach 10 million subscriptions for Tesla’s Full Self Driving product.
- Humanoid robotics: sell one million humanoid robots. Tesla has been developing a humanoid prototype called Optimus.
Shareholder opposition and governance concerns
Despite the vote outcome, several large institutional investors and proxy advisory firms opposed the package before the meeting. Their concerns included the size of the award, the realism of the targets, and how the board handled prior compensation approvals.
In an earlier case, a Delaware court invalidated a previous Musk pay package for weak board independence. That ruling is now being appealed by Tesla, and the new vote happened against that legal backdrop. The combination of shareholder approval and active litigation creates legal and public relations complexity for the company.
How feasible are the milestones
Assessing feasibility matters when compensation depends on outcomes. The milestones require growth at an unprecedented scale in several areas at once, including vehicle sales, a subscription model expansion, autonomous fleet deployment, and mass sales of humanoid robots.
- Robotaxi rollout: Tesla’s robotaxi concept depends on software, hardware, and regulatory approval across many jurisdictions. Current deployments are limited, and regulators have different standards that could slow broad service launches.
- Full Self Driving subscriptions: Tesla sells advanced driver assistance software under a subscription model. Reaching 10 million subscriptions implies wide consumer adoption and an effective product that meets safety and regulatory standards.
- Humanoid robots: Producing and selling one million humanoid robots would be a major manufacturing challenge. Robots must be affordable, reliable, and have clear customer use cases to reach that scale.
- Market cap growth: Increasing market capitalization more than fivefold requires sustained revenue growth, profitability, and investor confidence over a decade, while competing firms and macroeconomic factors could affect valuations.
Business context and near term headwinds
Tesla faces real business challenges today, which make some milestones look distant. The Cybertruck has had mixed early reception for some buyers. Tesla’s robotaxi service is not broadly available. Competition from Chinese EV makers is strong, and global subsidy and tax credit rules affect consumer demand. Those factors can slow the path to the targets in the compensation plan.
Comparison to historic executive compensation
Executives at major companies have received large stock based awards before, but this package stands out by potential size and by the breadth of its nonfinancial milestones. When measured in potential total value, it is larger than most past awards. That scale is one reason why governance groups and many investors scrutinized the deal closely.
Potential effects on markets and public perception
Shareholder approval may produce several outcomes for Tesla and for broader public views.
- Stock impact: the vote alone could boost investor sentiment in the short term by reducing headline uncertainty; long term market reaction will depend on Tesla’s business performance and whether the milestones appear achievable.
- Investor relations: many institutional investors are still concerned about governance; ongoing litigation and activism could persist following the vote.
- Employee morale: employees and prospective hires may interpret the package as a strong incentive to pursue ambitious projects, or as misaligned if nearer term business issues are not addressed.
- Public perception: the size of the award and the futuristic targets invite public debate about executive pay fairness and the societal trade offs of concentrating wealth.
Legal and regulatory next steps
Tesla has appealed a Delaware court ruling that voided a prior package. The company will also file a formal vote tally with the SEC. Those legal moves could influence how the new award is implemented and whether future challenges arise from shareholders or regulators.
Strategic implications for Tesla’s direction
The package links executive reward to Tesla’s ambitions in autonomous systems and robotics. That alignment signals that Tesla’s leadership is prioritizing long range bets on artificial intelligence driven services and consumer robotics. Whether that focus creates shareholder value depends on execution, technology progress, consumer adoption, and regulatory approval across many markets.
Short list of strategic trade offs
- High risk, high reward incentives can push aggressive investment in new technology; they can also divert resources from current products and operations.
- Tying pay to market cap places weight on investor sentiment and macro conditions, not only company fundamentals.
- Large awards to founders can discourage potential governance reforms, particularly when voting control remains concentrated.
Key takeaways
- Shareholders approved a new pay plan for Elon Musk with over 75 percent support, potentially creating a historically large award tied to ambitious targets.
- The milestones require major growth in market value, vehicle sales, subscriptions, robotaxi deployments, and humanoid robot sales within ten years.
- Legal challenges and investor opposition remain relevant, given a prior Delaware court ruling and unsettled governance concerns.
- The package may influence Tesla’s strategic focus, but delivering on the targets will depend on technical progress, regulatory approvals, and market competition.
FAQ
Will Elon Musk actually receive one trillion dollars?
The one trillion figure is an upper bound based on the potential value of all awarded shares if every milestone is achieved and if stock prices reach the levels implied by the award. The actual payout, if any, will depend on Tesla meeting specific targets and on the company stock price at the time shares vest.
Does this change Tesla ownership right away?
No. The vote authorizes the package and shares will only be issued if performance milestones are met. Until that happens, Musk’s current ownership stake remains largely unchanged.
Can shareholders challenge this after the vote?
Yes. Shareholders have previously pursued legal challenges to executive pay and governance actions. The package is also subject to regulatory filings and potential review if legal issues persist.
Conclusion
Tesla’s shareholder approval of Elon Musk’s new pay package is a major corporate governance event. The vote clears a procedural hurdle, but the outcome raises broader questions about how companies reward founders, how ambitious technological bets are incentivized, and how courts and investors balance growth ambitions with governance safeguards. For ordinary readers, the decision matters because it ties a top executive’s reward to technologies that could affect transportation, labor markets, and consumer devices over the next decade.
Watch for final SEC filings, the progress of Tesla’s appeal in Delaware, and the company’s public updates on robotaxi and humanoid robot development to see whether the milestones move from plan to reality.

Leave a comment