Overview: what YouTube and Google announced
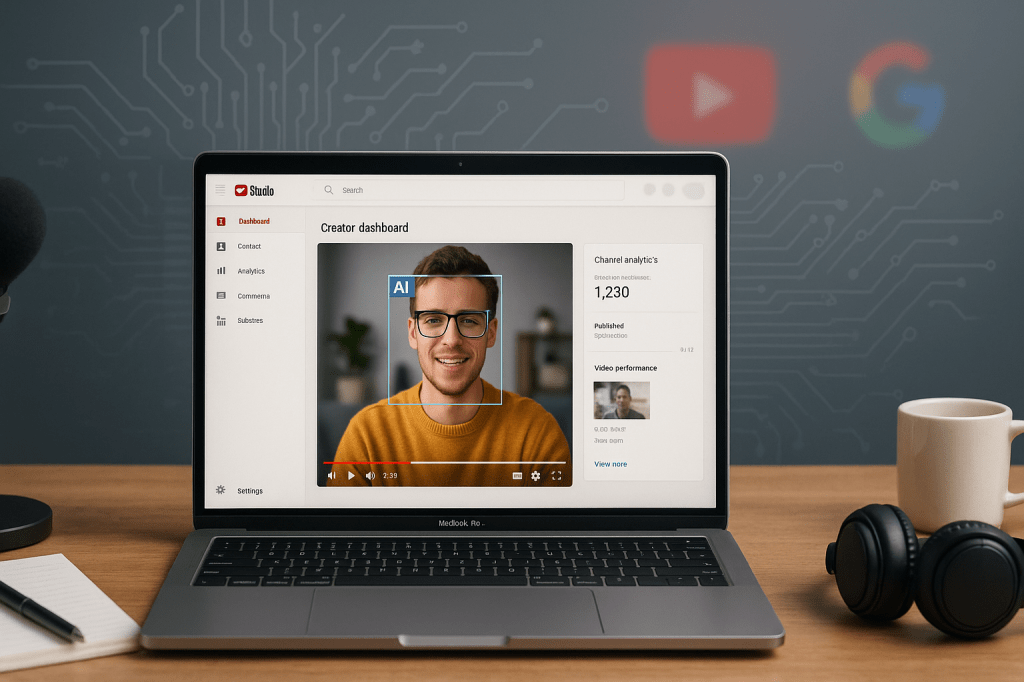
YouTube, part of Google, is rolling out a new AI-based likeness detection feature for creators in its Partner Program. The tool lets verified creators review videos that YouTube flags as showing their face or likeness. Creators can then request removals if the content appears to be a deepfake or otherwise misuses their image.
The feature was first tested with talent agencies and is now being offered to a first wave of creators. YouTube says the rollout will expand in phases over coming months. The system works in a way similar to Content ID, YouTube’s copyright matching tool; however, this new tool targets faces and likeness rather than copyrighted audio or video.
Why this matters to ordinary viewers and creators
Fake videos that put real people into fabricated scenes have become easier to make because of advances in generative AI. That can harm creators, mislead viewers, and spread false information. YouTube’s new tool gives creators a direct way to learn when their likeness shows up in other uploads, and to ask for those videos to be taken down.
For viewers, the change is about improving trust. Knowing a creator can flag and remove manipulated videos may reduce the reach of harmful or deceptive content. For creators, it adds a layer of control over how they appear on the platform, while also adding new responsibilities around verification and review.
How the likeness detection tool works
The system uses AI to scan uploads for faces or likenesses that match verified creators who opted in. When the system finds a potential match, YouTube notifies the matched creator and provides a place for them to review the flagged videos. The creator can then request that YouTube remove a video, if it violates platform rules or misuses their image.
Key workflow elements
- Verification. Creators in the Partner Program must verify their identity to participate. That verification is separate from simple account verification badges.
- Matching. AI evaluates uploaded videos and highlights potential matches to creators who opted in.
- Review and takedown. Creators receive a list of flagged videos and can request removal or appeal decisions through YouTube’s existing moderation processes.
Who gets access and how the rollout will proceed
YouTube is offering the feature first to a limited group of Partner Program creators and to talent agencies who worked in early tests. The company plans a phased expansion, meaning more creators will be able to opt in over the next few months. Exact timing and eligibility thresholds were not specified beyond Partner Program membership.
Creators who want access should watch YouTube’s Partner Program communications. Enrollment will require identity verification and agreeing to the tool’s use terms.
How this compares to Content ID
Content ID is YouTube’s long standing copyright matching system that identifies copyrighted audio and video and gives rights holders options to block, track, or monetize matches. The likeness detection tool is similar in workflow because it automatically finds possible matches and notifies the rights holder or creator.
The main difference is the focus. Content ID identifies copyrighted works. Likeness detection targets faces and personal appearance. The goal is to address privacy, impersonation, and deepfakes, not copyright claims.
Known limitations and false positives
YouTube warns the tool is not perfect. The AI can return false positives, flagging genuine, unaltered footage. That can happen when similar appearances, lighting, or camera angles confuse the matching algorithm.
Creators who receive notifications should expect some noise. False positives add workload for creators who must review flagged items. They also raise concerns about accuracy before broad deployment.
Privacy and verification concerns
The system requires creators to verify their identity in order to opt in. Verification can improve matching precision, but it also raises questions about how verification data is stored and used. Creators may worry about providing identity documents or other sensitive data to a large platform.
There are potential risks if verification data is mishandled, or if matching systems are expanded to scrape images without explicit opt in. YouTube has not indicated changes to how it stores verification data, but creators should watch for details on data retention and privacy safeguards.
Implications for deepfakes and misinformation
The tool is a practical step toward limiting malicious uses of generative AI on YouTube. By surfacing videos that use a creator’s likeness, the system can help prevent impersonation and reduce the spread of doctored content that misleads audiences.
However, the tool is not a complete solution. It focuses on creators who opt in and who are in the Partner Program. Videos that misuse the likeness of nonopted people, public figures who are not in the program, or ordinary people may not be caught. Deepfake creators can also alter or mask their outputs to evade detection.
Operational challenges for YouTube
Scaling this kind of system at YouTube’s size is difficult. Moderators will need to handle appeals and take down requests. The platform must balance fast responses with fair review, to avoid wrongful removals and to prevent abuse where someone might try to silence legitimate content.
Other challenges include:
- Appeals backlog, if many false positives generate requests.
- Abuse by bad actors who attempt to game the reporting system to target rivals.
- Integration with labeling, so that identified manipulated videos get appropriate context for viewers rather than simple removal in every case.
Practical steps creators can take now
If you are a creator or manage creator accounts, here are practical steps to prepare and respond.
- Check Partner Program status. Only creators in the Partner Program are eligible initially.
- Follow verification instructions carefully. Provide required documents through official YouTube channels and track how the data will be used.
- Document your original work. Keep original files and timestamps that prove content ownership and authenticity.
- Review flagged videos promptly. Expect some false positives and be prepared to use YouTube’s appeals process if a takedown is not justified.
- Set team roles. Assign someone to monitor incoming flags, handle reviews, and communicate with legal counsel if needed.
Wider industry context
Other platforms have been testing or deploying tools to identify manipulated media, and governments are discussing regulation for synthetic content. YouTube’s move is consistent with industry efforts to address AI generated misinformation, while balancing free expression and platform moderation duties.
Expect similar tools and policy updates from other social platforms. Researchers and advocacy groups will continue to evaluate accuracy, fairness, and the societal effects of automated detection systems.
What to watch next
- Expansion timeline. Watch for announcements about when more creators can opt in.
- Accuracy improvements. YouTube will likely refine the model to reduce false positives.
- Transparency reporting. Look for public metrics on takedowns, false positive rates, and appeals.
- Third party integrations. Developers and agencies may offer tools to help creators manage flagged content.
Key takeaways and FAQ
Key takeaways, in brief:
- YouTube is launching a likeness detection tool for creators in its Partner Program. The tool notifies verified creators when their face or likeness appears in uploaded videos.
- Creators can review flagged content and request removals. The experience will resemble Content ID workflows, but the focus is on personal likeness rather than copyright.
- The system has limits, including false positives and scope restricted to enrolled creators. It is not a universal fix for deepfakes or misinformation.
FAQ
Who can use the tool right now? Creators enrolled in YouTube’s Partner Program and included in the first rollout wave, plus partners who joined early tests.
Will this stop all deepfakes? No. The tool helps creators find and remove videos that use their likeness, but detection is imperfect and many manipulations may still slip through or target people outside the program.
How does a creator enroll? Creators must verify their identity through YouTube’s verification process and opt in. Check YouTube’s Partner Program notices for specific steps.
Conclusion
YouTube’s new AI likeness detection is a measurable step toward giving creators more control over how their image is used. The tool aligns with broader efforts by Google and other platforms to manage AI generated content through detection, labeling, and updated policies.
The feature will not solve all problems associated with deepfakes. It has technical limits, privacy questions, and operational challenges. Still, for creators who rely on YouTube, it offers a new option for finding possible impersonations and requesting removals. Watch for phased expansion, accuracy improvements, and transparency updates as the system matures.

Leave a comment